Control & Monitor IoT Devices Remotely: A Complete Guide
In an increasingly interconnected world, where devices communicate and interact without human intervention, have you ever pondered the possibilities of controlling and managing these "smart" entities from a distance? The ability to remotely access and manipulate Internet of Things (IoT) devices isn't just a convenience; it's a transformative shift that unlocks unprecedented levels of control, efficiency, and functionality, streamlining operations and empowering users like never before.
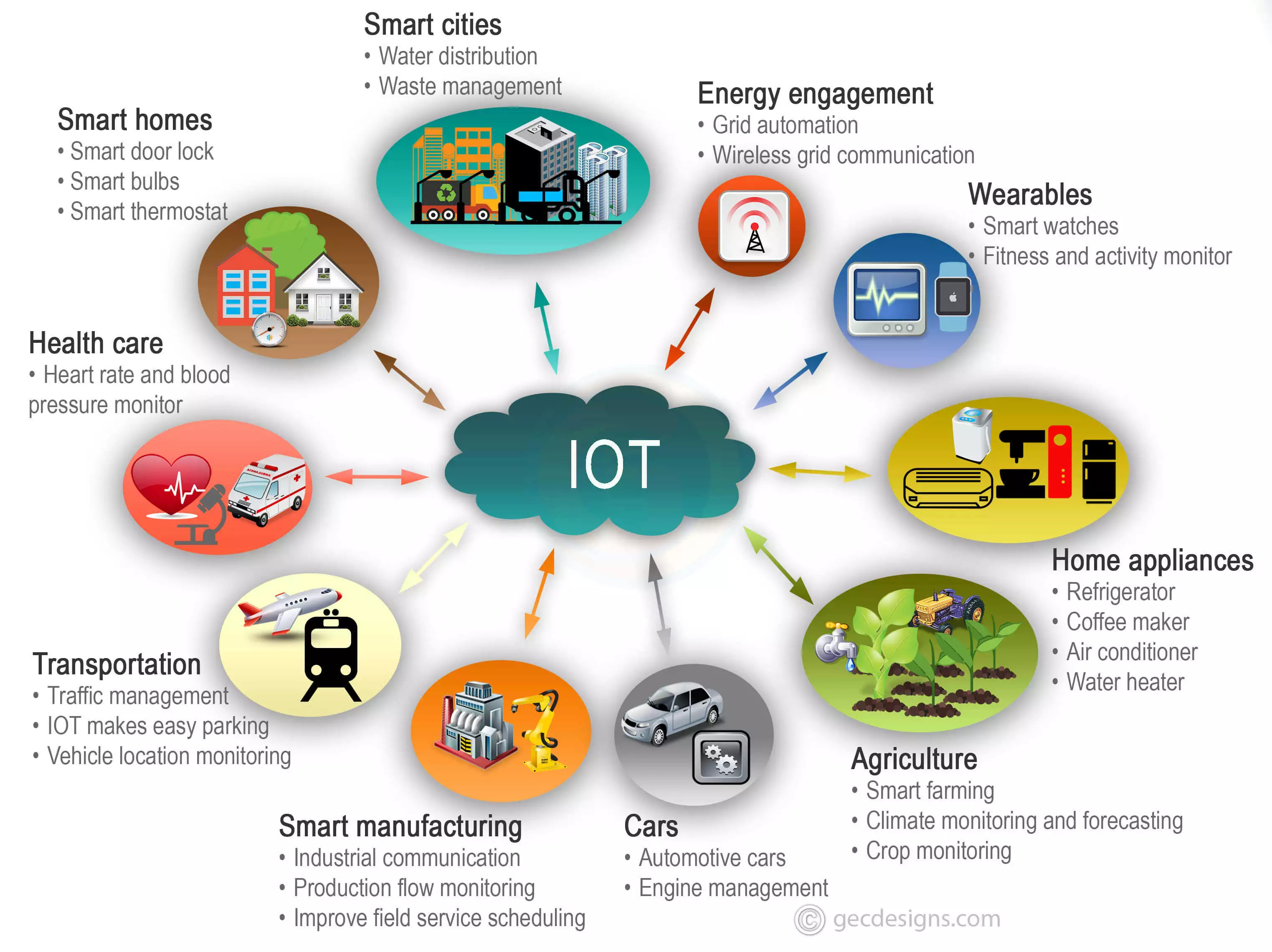
The evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) has ushered in an era where everyday objects, from household appliances to industrial machinery, are equipped with sensors, actuators, and communication modules. This technological leap has sparked a demand for robust remote management capabilities, allowing users to interact with these devices irrespective of their physical location. Remote functionality, in essence, becomes the cornerstone of seamless connectivity and control within the IoT ecosystem, providing users with unparalleled access, monitoring, and management options. This paradigm shift not only enhances the user experience but also opens up new avenues for innovation across various sectors.
At the heart of effective IoT management lies the ability to control and monitor devices remotely. This capability is achieved through a range of protocols, each with its own strengths and applications. This allows for the management of devices from anywhere, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
- Teach Me First Honey Toon Can Jaehong Succeed Read Now
- Explore Free Movies Alternatives To 1tamilblasters More
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Functionality | Combining remote control with comprehensive monitoring capabilities, all accessible from a single, intuitive dashboard. This empowers users with a holistic view of their IoT ecosystem, simplifying management and control. |
| Monitoring Features | Real-time monitoring of critical device metrics, including CPU usage, memory consumption, and network performance. This proactive approach allows for immediate identification of potential issues and ensures optimal device operation. |
| Alerting and Automation | Configurable alerts based on real-time data from monitored IoT devices, enabling automated actions such as batch job execution. This advanced feature streamlines operations and reduces manual intervention. |
| Extended Capabilities | Going beyond traditional screen sharing, offering terminal access, application control, and edge management functionalities. This comprehensive solution addresses complex IoT management scenarios with ease. |
| Accessibility | Remote access and control of smart devices from any location, whether it's across the room or across the globe. This enhances user flexibility and convenience. |
| Relevance to IoT | Plays a vital role in enabling seamless connectivity and control of IoT devices and systems from a distance. This functionality is crucial for the success of the IoT landscape. |
| User Benefits | Users can remotely access, monitor, and manage IoT devices, applications, and processes, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and overall functionality. |
| Popular Protocols | Numerous protocols support remote access to IoT devices, each tailored to specific use cases. These protocols enable flexible and efficient device management. |
Reference: Example.com
Several established protocols facilitate the remote management of IoT devices, each offering unique characteristics tailored to different operational requirements. For instance, protocols such as SSH (Secure Shell) provide secure, command-line access to devices, enabling users to execute commands, manage files, and troubleshoot issues. Alternatively, protocols such as VNC (Virtual Network Computing) provide a graphical user interface (GUI) for remote desktop access, permitting users to visualize and interact with the devices screen as if they were physically present. Other protocols like MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) facilitate lightweight messaging, ideal for transmitting sensor data and control commands over constrained networks. The choice of protocol often depends on the specific application, the level of security required, and the bandwidth constraints of the network.
Remote access is far more than a convenient feature; it's a crucial element for enhancing efficiency and convenience in managing IoT devices. It allows users to interact with their devices from virtually anywhere, streamlining operations, and improving user experiences. For example, a homeowner can adjust their thermostat remotely, a farmer can monitor and control irrigation systems from a mobile device, and a technician can troubleshoot industrial machinery without being physically present. This heightened control reduces downtime, cuts operational costs, and enables proactive management. As the IoT landscape evolves, remote access will continue to play a central role, shaping the future of connected technologies.
- Best Ai Clothes Removers Tools Techniques In 2024
- Kaitlyn Krems Onlyfans Latest Leaks Nude Videos Revealed
Now, lets delve into the practical steps involved in setting up remote access for your IoT devices. Setting up remote access for your IoT devices may vary depending on the specific device and manufacturer, but here are some general steps to ensure a smooth setup:
- Device Compatibility: Ensure that your IoT device supports remote access functionalities, such as internet connectivity and remote control features. Verify your device's documentation for supported protocols and setup instructions.
- Network Configuration: Confirm that both your IoT device and the device you intend to use for control (e.g., smartphone, computer) are connected to the internet.
- App Installation and Setup: Most IoT devices come with a specific mobile application or web interface for remote control. Download and install the appropriate app on your controlling device.
- Account Creation: Within the app or web interface, create an account and register your IoT device following the manufacturers instructions.
- Device Pairing: Follow the instructions to pair your IoT device with the control app. This may involve entering a pairing code, scanning a QR code, or configuring network settings.
- Configuration of Remote Access: In your app or web interface, configure the remote access settings. This may involve setting up a secure connection and enabling remote control permissions.
- Testing the Connection: Once configured, test your remote access functionality. Verify that you can view sensor data, send control commands, and remotely manage your IoT device.
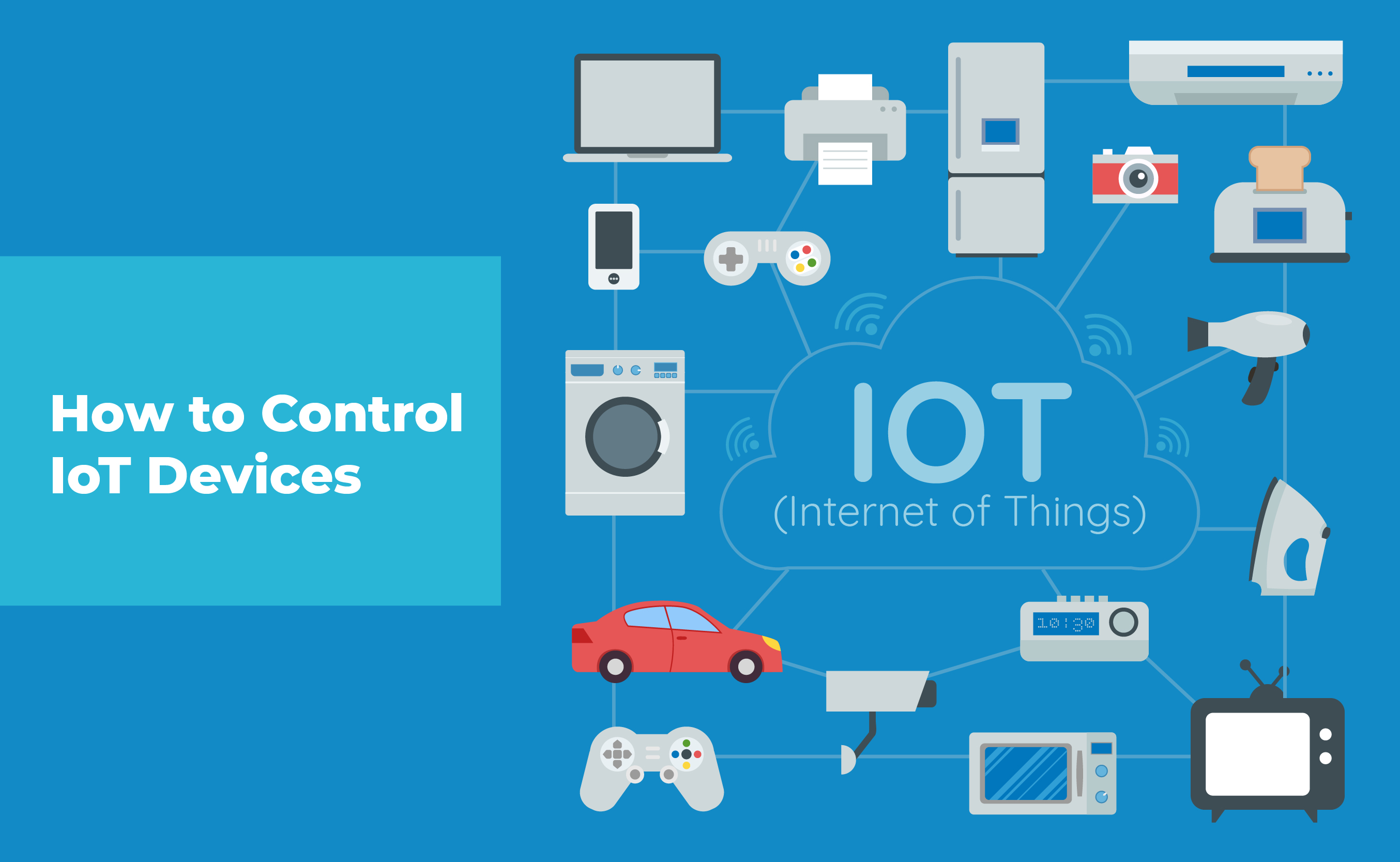
Unlike the traditional remote controls, IoT remote controls leverage internet connectivity, enabling device control through mobile and web interfaces. Users can engage with their devices from any location with an internet connection, providing unparalleled flexibility and control. The capacity to view sensor data (such as temperature readings) and send control commands (such as adjusting the thermostat) enhances the user experience, promoting both convenience and operational efficiency.
Numerous methods are available for remotely managing IoT devices. Smartphone applications serve as a central control center for various IoT devices, allowing users to view sensor data and send control commands wirelessly. In addition, most IoT devices permit remote access control, granting users the ability to conveniently access and control their devices remotely via mobile apps or web interfaces. In essence, the accessibility of the Internet is the only prerequisite.
Most IoT devices are designed with communication modules, enabling them to connect to the internet and be controlled remotely. Initiating control over the internet typically involves the following steps:
- Connectivity: Ensure that both the IoT device and the device you are using for control are connected to the internet.
- App or Web Interface: Utilize the specific app or web interface provided by the device manufacturer.
- Authentication: Log in to the app or web interface using your credentials, such as a username and password.
- Device Selection: Select the IoT device you wish to control from within the app or web interface.
- Command Execution: Send control commands, view sensor data, and configure settings according to your needs.
To take a practical look at remote control options for IoT devices, consider the following scenarios:
- Mobile Apps: Most IoT devices are paired with specific apps that you can easily install on your smartphone. Through these apps, you can control and manage your devices.
- Data Monitoring: Parameters like temperature, pressure, current, voltage, and humidity can be monitored remotely.
- Web Interfaces: Access and control IoT devices through web-based dashboards.
To successfully control and manage your IoT devices remotely, or even locally, using a variety of methods and technologies, a structured approach is essential. The integration of sensors and actuators into physical devices, connecting these to a network infrastructure, and ensuring remote accessibility through a software interface is key. Secure device authentication and authorization are essential to protect against unauthorized access. Moreover, the adoption of best practices will optimize performance and ensure the seamless functioning of IoT remote control.
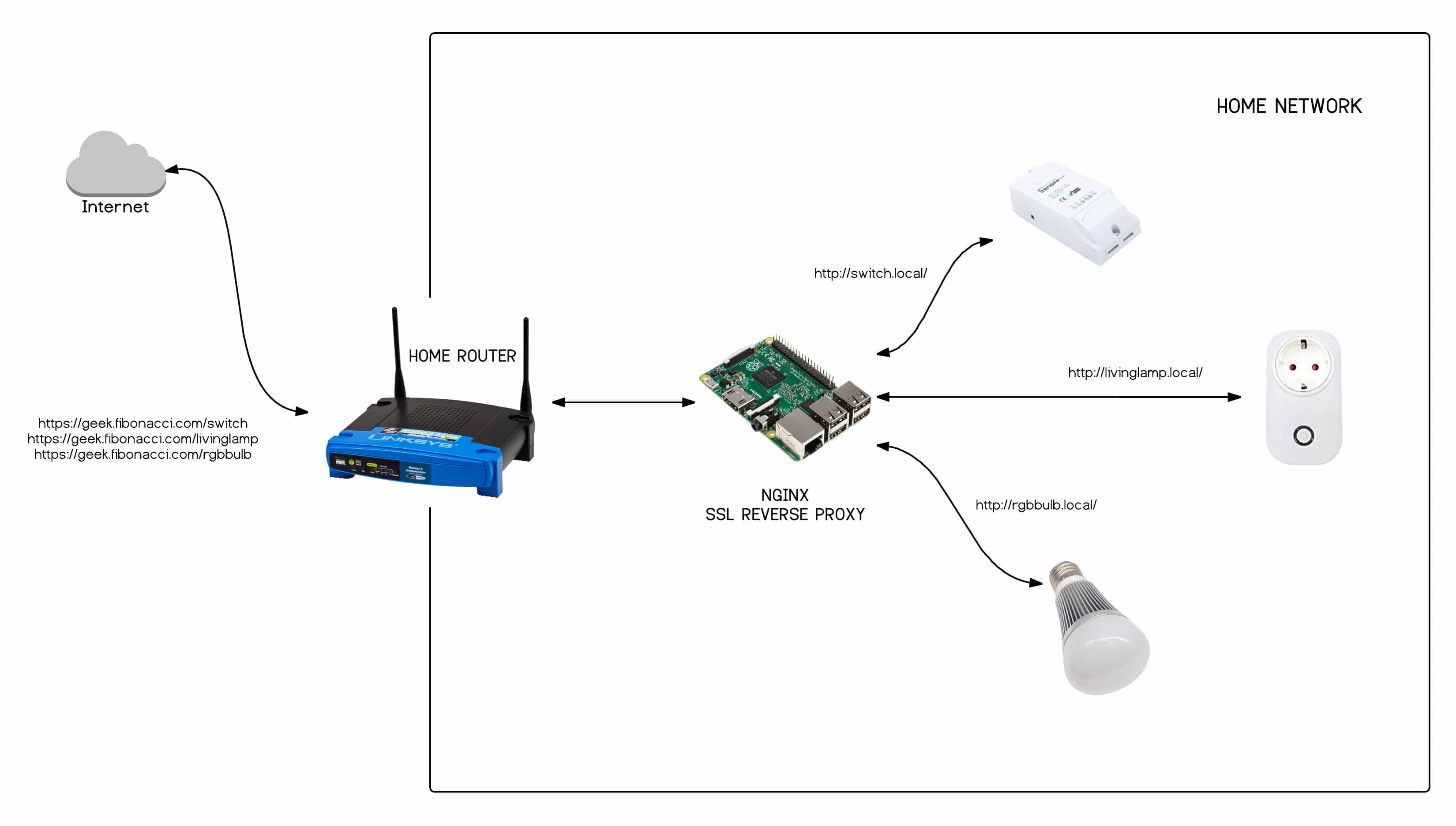
For those seeking a secure way to remotely access IoT devices, solutions like Qbee.io offer a secure, integrated remote access solution, allowing access to any device port, even behind firewalls. Alternatively, Blynk allows users to remotely control and monitor IoT devices through a mobile app, providing an easy way to create interactive user interfaces for IoT systems. SocketXP is another cloud-based solution that provides SSH access to remotely located IoT devices, such as Raspberry Pi, Arduino, NVIDIA Jetson, or any embedded Linux devices behind a NAT router or firewall. Using secure SSL/TLS VPN tunnels makes remote access simple and secure. These are just a few examples of how IoT remote access solutions are implemented.
Detail Author:
- Name : Prof. Woodrow Kemmer II
- Username : haley.hermann
- Email : adaline26@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 2000-01-01
- Address : 90116 Dora Ramp Lake Anika, HI 46750
- Phone : +1-707-263-3240
- Company : Kassulke-Larson
- Job : Producer
- Bio : Impedit numquam quos dolor optio repellat. Ratione officia qui occaecati pariatur voluptate explicabo nisi. Alias vero voluptatem aperiam id tempora.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/kaysanford
- username : kaysanford
- bio : Non nihil est et et. Nesciunt accusantium dolor aut quaerat maiores.
- followers : 5698
- following : 1888
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/ksanford
- username : ksanford
- bio : Delectus sint aliquid delectus ut.
- followers : 3670
- following : 980
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/sanfordk
- username : sanfordk
- bio : Et libero hic voluptatibus neque et necessitatibus beatae.
- followers : 1348
- following : 423
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@kay4823
- username : kay4823
- bio : Earum occaecati voluptas adipisci.
- followers : 1755
- following : 1011